Causes of corneal ulcers
Corneal ulcers, or the milder keratitis, can develop due to trauma to the cornea, eyelid disease, severe dry eye, fungal infections, herpes simplex viral infections, and other causes.
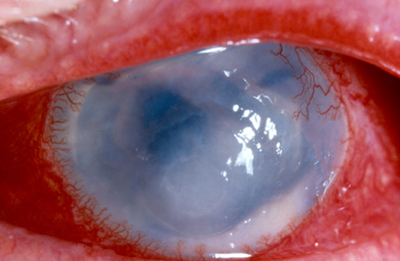
There are two prevalent types of corneal ulcers. Infectious ulcers (bacterial or fungal) tend to be painful, and in some cases, if left untreated, can cause severe damage or even corneal perforation. Sterile ulcers, on the other hand, usually cause little or no pain.
Improper care and handling of contact lenses, which can lead to infection, are often causes of corneal ulcers.
Symptoms of corneal ulcers
The symptoms of corneal ulcers may include:
- pain;
- redness;
- blurred vision;
- tearing;
- discharge; and
- sensitivity to light.
Treatment of corneal ulcers
Treatment for corneal ulcers depends on the cause. It typically includes steroid eye drops, anti-inflammatory drops, or antibiotics. Initial use of steroids alone for some types of ulcers can cause the infection to spread or prevent the cornea from healing, resulting in rapid worsening. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to administer eyedrops every hour around the clock, intravenous antibiotics, and other treatments. In rare instances when the cornea is severely damaged, a corneal transplant may be necessary to improve vision. © 2025, 2015 Dr. Robert Schertzer Inc. based on 2007 The American Academy of Ophthalmology
